
www.eurowilson.org
Pregnancy
Treatment must be continued throughout pregnancy, because of the risk of fulminant liver failure if it is stopped. Many successful pregnancies have occurred in women treated with anti-copper drugs. Infants of Wilson's disease mothers present no particular problems. Assuming that there is no parental consanguinity, the risk that the baby has Wilson's disease is approximately 1:200; though all will be obligate heterozygotes (i.e. will carry the genetic fault see diagrams VI-VII). Breast feeding is not contraindicated.
Diagram VI
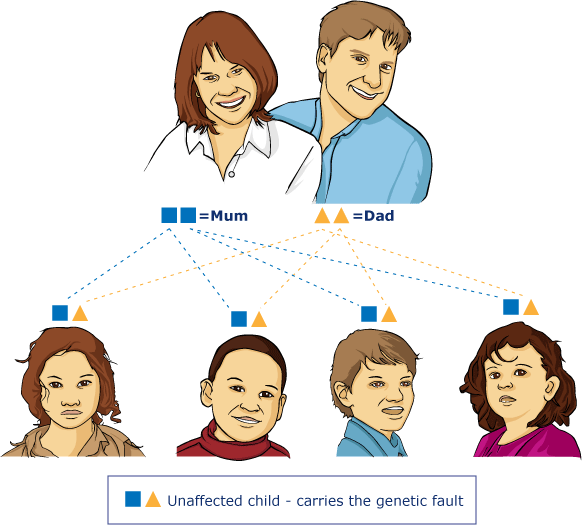
In this example dad has Wilson's disease (2 orange triangles). Each baby will be an obligate heterozygote. That is to say the child will be unaffected but carry the genetic fault (one orange triangle and one blue square).
This is just an example; it would also have been the same outcome if mum had Wilson's disease and dad did not.
Diagram VII
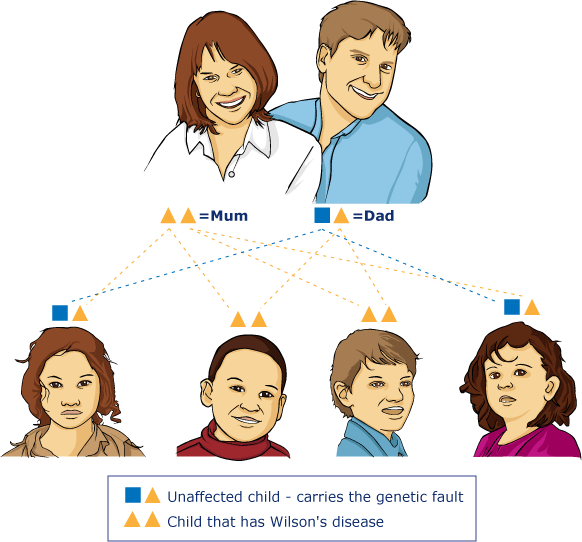
In this example mum has Wilson's disease (2 orange triangles) and dad is an unaffected carrier of the genetic fault. In this example there is a 50% probability that the baby will inherit Wilson's disease.